
FIGHTING THE DIABETES EPIDEMIC – EARLIER IT IS DETECTED, BETTER THE CHANCES OF REVERSING IT
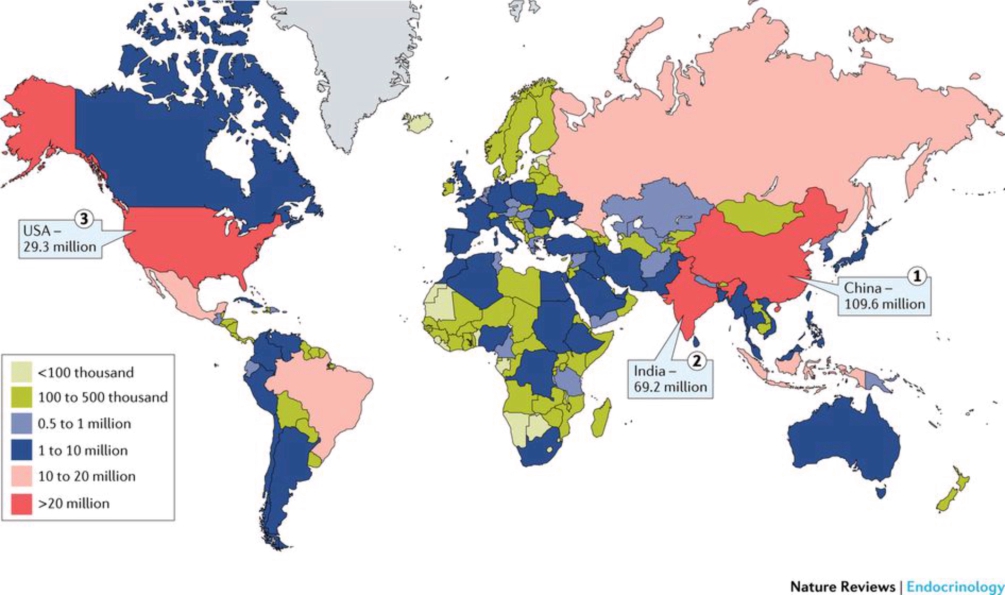
- India is rapidly becoming the capital of diabetes in the world.
- About 73 million Indians affected by Diabetes Mellitus says statistic by the “IDF”[1]
- 1 out every 2 people having diabetes across the globe, are undiagnosed.[2]
Reasons?
- 79% of all people having diabetes are from low or middle income countries.[2]
- Negligent outlook towards regular body checkups

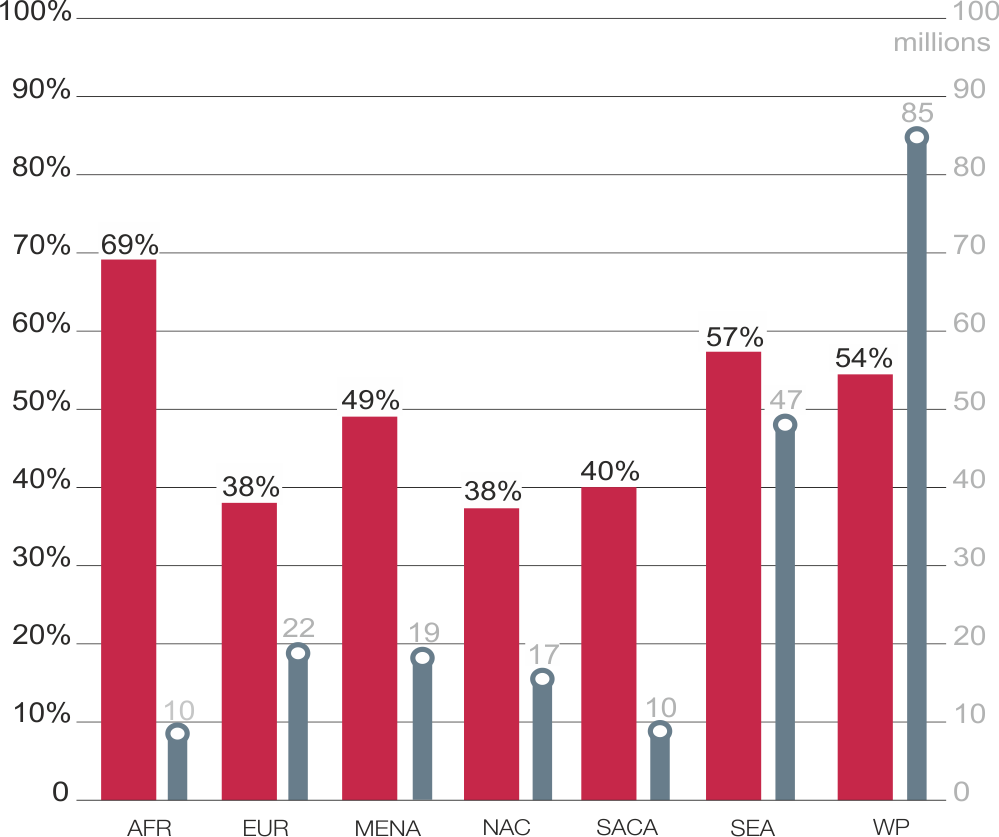 Undiagnosed percentage and undiagnosed cases of diabetes (20-79 years) by region[1]
Undiagnosed percentage and undiagnosed cases of diabetes (20-79 years) by region[1]
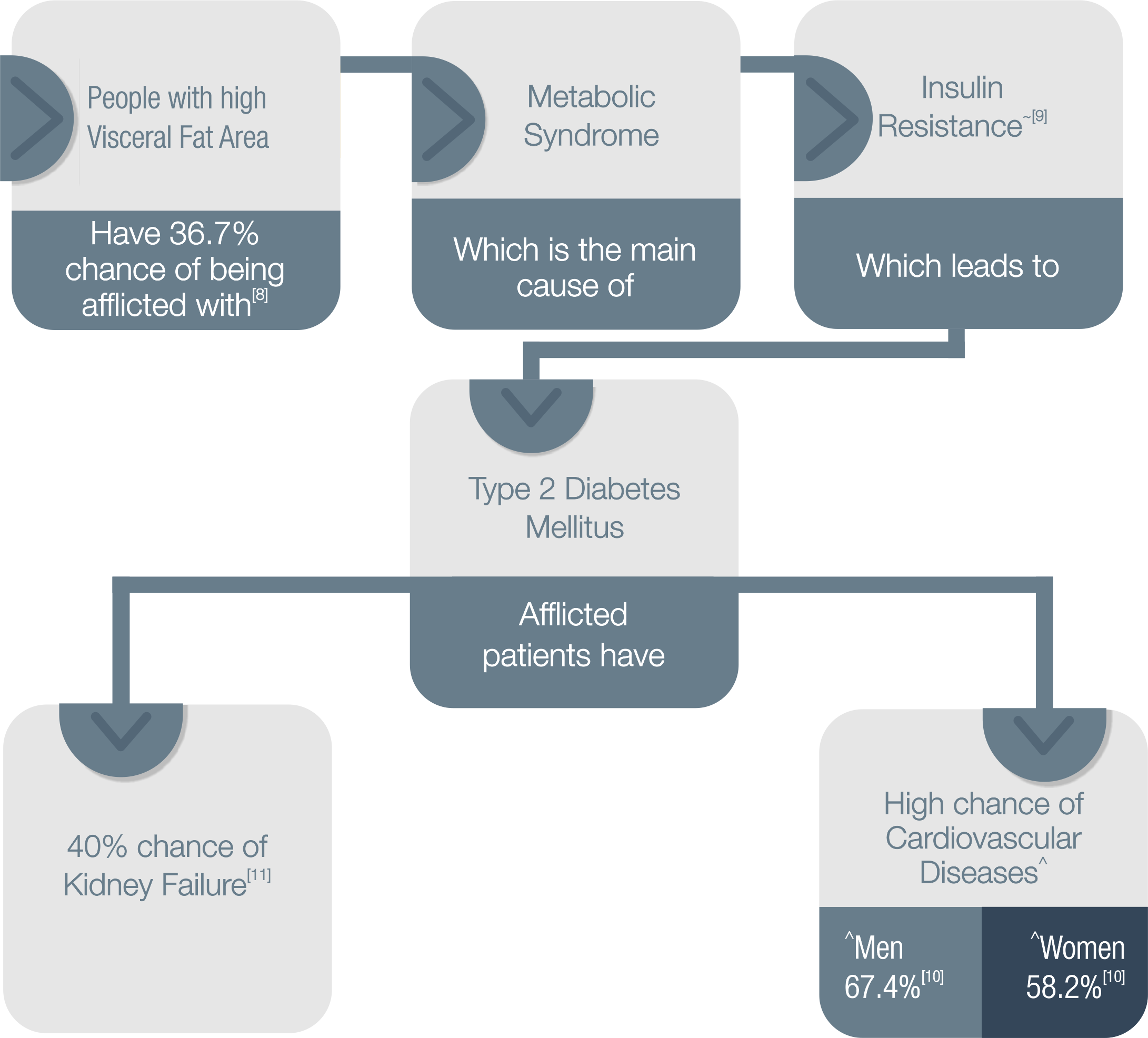
3 markers of diabetes that InBody monitors:
- Leg Muscle Mass
- Visceral Fat & Percent Body Fat (PBF)
- Extra Cellular Water (ECW) Ratio
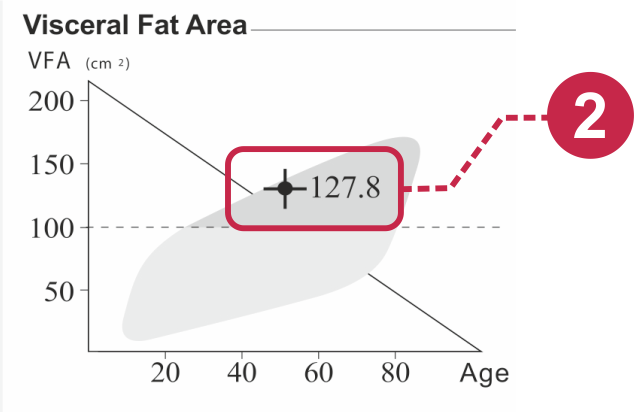
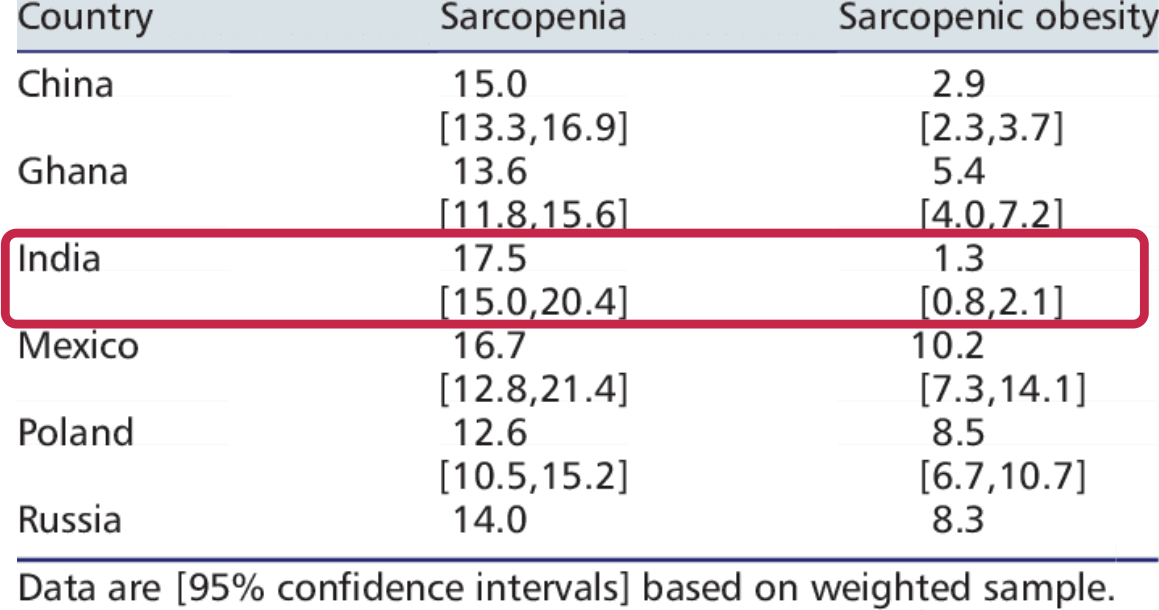
17.5% of Indians at or below the age of 65 years are sarcopenic[3], which is the decline of muscle mass in a person’s body
Causes:
- Aging
- Under nutrition
- sedentary lifestyle
- nflammation
- oxidative stress
- decreased testosterone[4]
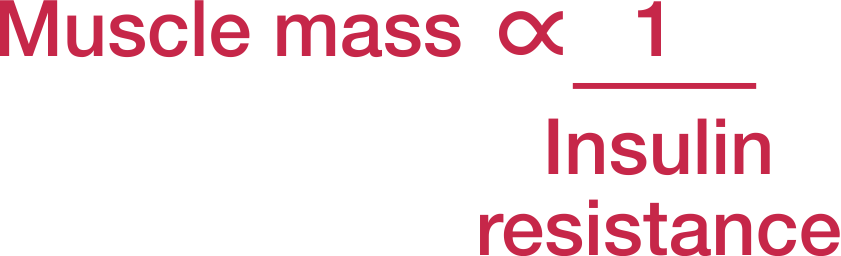
Skeletal muscles are the primary site of insulin [4] stimulated glucose disposal at euglycemia.[4]
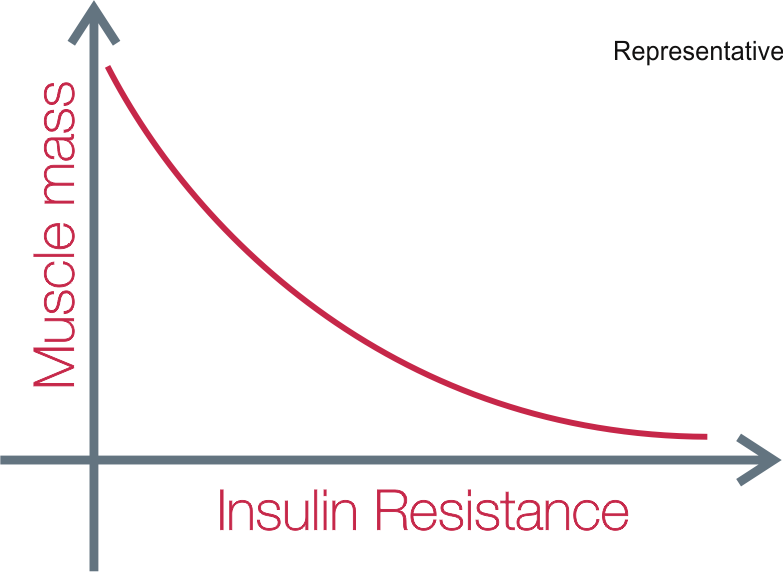
RESEARCH POINTS
Patients afflicted with diabetes have 2 times the loss in thigh muscle, as compared to people who don’t have diabetes[5]
For people with BMI in normal range – higher thigh muscle area recommended to prevent insulin resistance.
For obese/ overweight people – higher thigh muscle area could be cause for concern.[6]
InBody APPLICATION
- Lower Leg Muscle Mass could be an early indicator for Type 2 diabetes, which can be monitored through Body Composition Analysis.
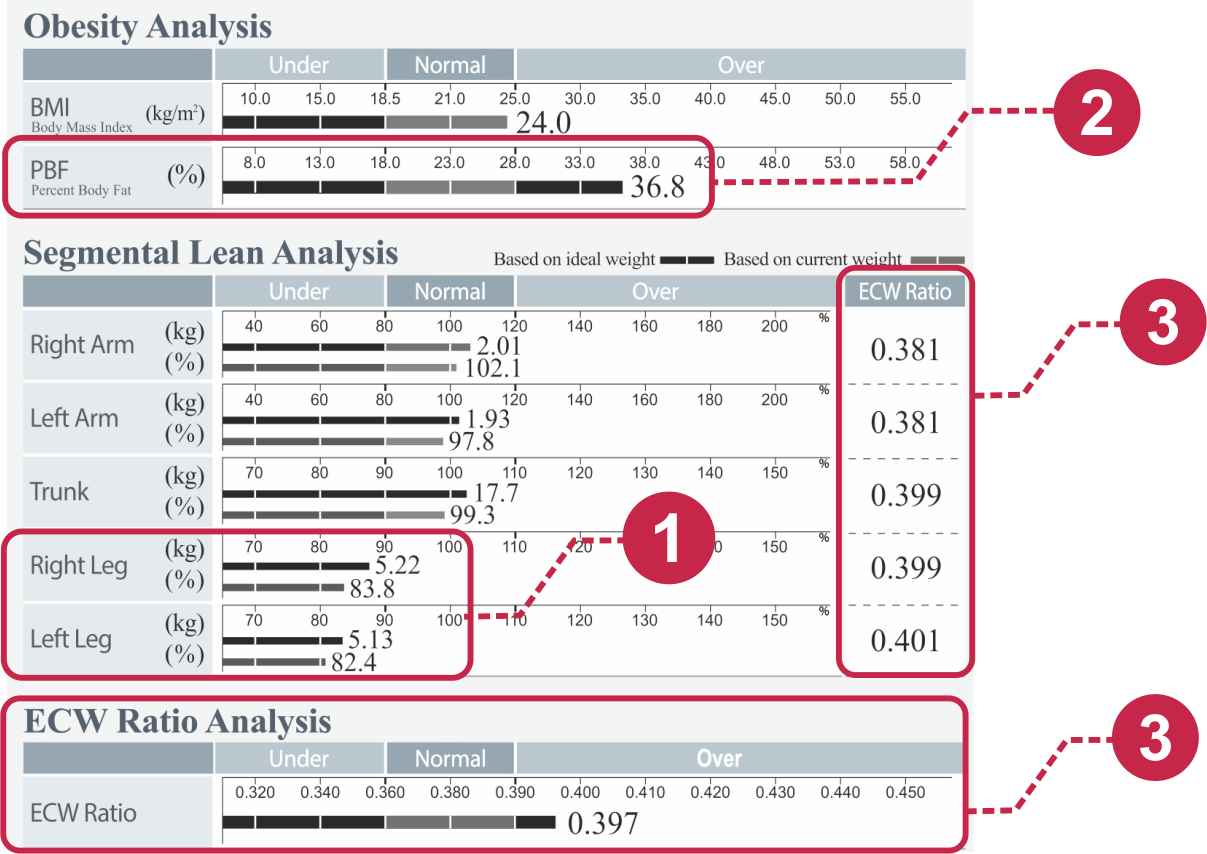
- InBody gives a comprehensive and detailed segmental lean analysis – within 60 seconds – of the Right Leg, Left Leg, Right Arm, Left Arm and Trunk.
- Muscle mass below 90% in legs, and SMI values below or close to 7.0 kg/m2 in men and 5.7 kg/m2 in women can be considered to be a red flag and the subject can be advised further tests.[7]
RESEARCH
- *A research conducted on 198 peritoneal patients (141 non diabetics and 57 diabetics) concluded that the ratio of ECW to TBW is higher in diabetic patients 0.40 ± 0.01 vs 0.39 ± 0.01 for men; 0.39 ± 0.01 vs 0.38 ± 0.01. Hence proving a direct relation between the ECW ratio and diabetes mellitus[12]
- *Percent Body Fat is a better indicator of cardiovascular risk factors than BMI[13]
- A research published in the Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice Journal, studied 61 patients with untreated DM. To calculate the M/I value as the insulin resistance reference indicator, elementary Body Composition was measured by impedance analysis using InBody 770. The study concluded that “Muscle/Fat ratio derived from InBody770 is useful as a clinical surrogate indicator of insulin resistance in type 2 DM”.[9]
REFERENCES
- https://www.idf.org/our-network/regions-members/south-east-asia/members/94-india
- https://www.idf.org/aboutdiabetes
- Stefanos Tyrovolas et.al; Factors associated with skeletal muscle mass, sarcopenia, and sarcopenic obesity in older adults: A multi-continent study; Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle 7(3):n/a-n/a· October 2015
- Seung Won Lee et.al; Appendicular Skeletal Muscle Mass and Insulin Resistance in an Elderly Korean Population: The Korean Social Life, Health and Aging Project-Health Examination Cohort; Diabetes Metab J; 2015; Page No. 38
- Seok Won Park et.al; Excessive Loss of Skeletal Muscle Mass in Older Adults With Type 2 Diabetes, Diabetes Care. 2009 Nov
- Seung Jin Han et.al; Association of Thigh Muscle Mass with Insulin Resistance and Incident Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Japanese Americans; Diabetes Metab J. 2018 Dec
- J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2014 Feb;15(2):95-101
- Seok Hui Kang et al; Association of Visceral Fat Area with Chronic Kidney Disease and Metabolic Syndrome Risk in the General Population: Analysis Using Multi-Frequency Bioimpedance; Kidney Blood Press Res 2015; 40:223-230
- Noboru Kurinami et al; Correlation of body muscle/fat ratio with insulinsensitivity using hyperinsulinemiceuglycemicclamp in treatment-naive type 2 diabetes mellitus; Diabetes and Research Clinical Practice 120 (2016) 65-72
- Dr. Anoop Dinesh Shah et al; Type 2 diabetes and incidence of cardiovascular diseases: a cohort study in 1·9 million people; The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology Volume 3, Issue 2, February 2015, Pages 105-113
- https://www.kidney.org/atoz/content/diabetes
- Davenport A. et al; Does Diabetes Mellitus Predispose to Increased Fluid Overload in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients? Nephron Clin Pract 2010;114:c60–c66
- Qiang Zeng; Percent body fat is a better predictor of cardiovascular risk factors than body mass index; Braz J Med Biol Res. 2012 Jul; 45(7): 591–600

Leave a Reply